
Speed is one of the primary signals for ranking in Google SERPs. Despite this, websites we can find hardly become serious about it. If you take a closer look, your website has considerable room for improvement in loading speed. Let’s take a look at these minor yet important details that can significantly decrease the site loading time and boost your SEO.
Know where you stand right now-

Google Analytics is a tool that can tell everything you need to know about your website Insight. If you have a Google Analytics setup for your website, you can easily find the current speed optimization level.
The Google Analytics report will show you your best pages and their performance stats. These stats are also complemented with some tips to improve your current optimization. By doing so, you will be able to list the pages you want to work upon on a defined priority level.
Once you know about which pages need your attention, your next step is to debug the causes that prevent your pages from loading faster. The stats will help you find out the culprits.
Now, when you know the culprits, you can prepare your strike plan and budget according to the priorities for each of them. You can also guess the required time for each of the fixes.
If possible, better you look for an alternative to JavaScript in some cases-
Pre-loading of images is a significant way to optimize the page loading speed. Some of the sites, use JavaScript to pre-load the images. Though JavaScript pre-loads can help you reduce the load time, most of the time it fails to serve the purpose. Why? Because web browsers have settings to disable JavaScript. Tech-savvy users who know about it, prefer to keep it disabled. Thus, even if you have used a significant tool to optimize the loading of images, it proves to be of no use in most of the cases.
Is there an alternative? Yes, there are ways to pre-load images on the pages using CSS. So, it’s better to utilize the considerations for all the browsers and users, and use a CSS alternative that is supported by all of them.
Are your images optimized?
Everyone knows that images should be well optimized for a faster page-loading. But what are these optimizations? Is it the file size or the image resolution? The answer lies in both. You must have seen an image with 150×150 resolution, but still, has the size of 2 MB or more.
It is because the images have been optimized regarding a desired resolution, but the physical size of the image has not been optimized. Yes, you guessed it right. Image size compression is the phenomenon I am talking about. You have got a hassle free access to the software like Adobe PhotoShop which can be used to compress the size and resolution of the images. Windows picture manager or paint brush can also be used for the same.
Depending on your desired picture dimension, 20-50 KB file size is desirable. Off-course, an image resolution of 1080×720 will have bigger size than that. But compressing the physical size of the image file will help the page load faster as compared to the uncompressed file.
Minification of codes is important-
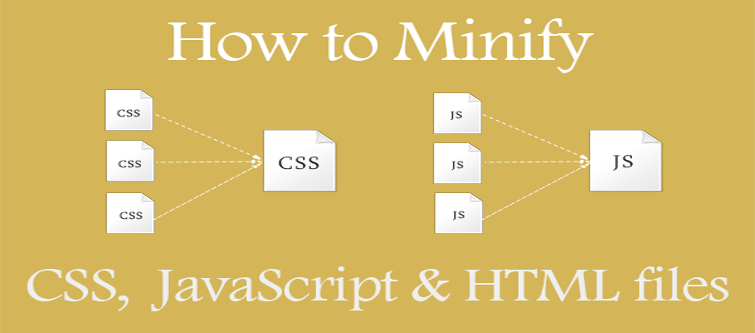
While building a website, we use thousands of line of codes. There is no issue in it; not at all. When these codes become redundant, they start to bother your page loading speed. Small redundancies multiply to become tenfold if you do not follow the proper coding standards.
W3C standards say that you should follow the method of code minification to reduce the number of lines or codes(specially in case of JavaScript). If you want to create a real faster loading page, then you have to follow it from the start till end. For example, use of inline CSS is not recommended in all the cases. Using inline CSS for each of the blocks or Divs will increase the code bloating, this will make the browsers confused about what CSS it has to use.
By doing a proper planning and execution, you can minimize the CSS codes by using CSS minification that will cover multiple elements. For example, instead of using inline CSS codes of each text box separately, you can use the CSS classes to style each of the text boxes in the page or website at one go. Thus, minimizing the redundant CSS codes that could have caused a bloat.
Over-implementation of JavaScript and CSS-
To make the sites more engaging and interactive, webmasters may use a bunch of CSS and JavaScript files. You should remember that the more JavaScript on your site, the more it will cause bottleneck to the server. Thus, it will decrease the site speed on the whole. Same is the case with CSS overuse.
You can minimize the CSS codes by following the approach explained in the previous point. For JavaScript, make sure that your server checks only 2 or three JavaScript files at once to avoid the bottlenecks.
To conclude
By no means, it is possible to attention a hundred percent automation of these small yet significant tweaks. You have to do it manually and right from the development phase. Even a smaller improvement in your approach can help you gain a significant propulsion in the site loading speed. Thus, improving your search engine optimization on the whole.








